Microbiology ‐ Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV)
The Infectious Bronchitis Virus is a coronavirus in the order Nidovirales. Coronaviruses have an envelope surrounding an RNA genome and are divided into 3 main groups designated alpha, beta and gamma. IBV is a gamma coronavirus.
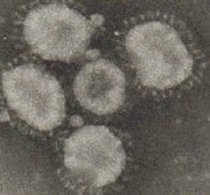
Properties
- Pleomorphic, but mostly rounded, “enveloped” virus with spikes on its surface.
- Contains a single stranded, positive sense RNA genome (see below) and codes for the viral polymerase (Replicase 1a/1ab), and structural proteins spike, envelope, membrane and nucleocapsid.
- Family: Coronaviridae.
- Rather fragile virus, infectivity of the virus is easily lost emphasizing the need to properly handle live vaccines.
- Able to withstand pH ranges of pH 2 ‐ 12 depending on the strain, temperature and time of exposure.
- Inactivated after 15 minutes at 56°C and after 90 minutes at 45°C.
- Sensitive to most common disinfectants.


