Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV)
Strains of IBV can also be classified based on genetic characteristics of the spike glycoprotein gene, which for the most part correlates with serotype.
Virus and Protein Structure
Four structural viral proteins designated S, M, E and N have been recognized.
- S – spike glycoprotein ‐ virus attachment and neutralisation epitopes.
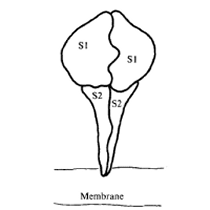
- Spike contains a receptor binding domain (attaches virus to host cell), cleavage site (junction between S1 and S2 subunits), fusion peptide and heptad repeats (facilitates entry of the virus into the host cell), transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic tail (anchors spike to the viral membrane).
- M – membrane protein ‐ integral membrane protein.
- E – envelope (small membrane) protein ‐ important for virus assembly.
- N – nucleoprotein ‐ surrounds and protects the viral RNA genome.